The Indian insurance industry began a significant transformation two decades ago, starting with privatization which expanded the number of insurers to almost 70. Consolidation among different stakeholders such as brokers, agents, and web aggregators into insurance ecosystems allows insurers to serve millions of underserved customer cohorts, and regulations driven by the Insurance Regulatory & Development Authority of India (IRDAI) focused the industry on best practices and gold standards.
Despite this evolution, ongoing digitization is the most crucial transformation lever within the industry, turning data into a strategic asset. However, due to the vast amount of critical personal information insurers collect —including financial, behavioral, social, and health-related data— insurance has become one of the most targeted industries by cybercriminals. To secure customer trust and continue the digitization curve, it was necessary to regulate, monitor, and control the use of data in its five stages: at source, in motion, in use, at rest, and at destruction.
Although the IRDAI had guidelines that mandated insurers to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, security, and safety of personal data collected for business use, there was no overarching law outlining clear boundaries on what constitutes the use or misuse of data.
In August 2023, India passed the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill (DPDPB), equivalent to the European Union’s 2018 General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The law (summarized in the figure below) mandates that enterprises seek explicit consent from individuals (or data principles), outline the purpose for which the data will be used, and provide the option of revoking this consent at any given time. The law also focuses on enterprises working with ancillary units or third-party entities to enforce adequate controls and checkpoints that ensure data privacy and safety. More importantly, the law sets down localization rules based on the criticality of data and enforces enterprises to oversee the movement and storage of personal data at their disposal.
Highlights of DPDPB
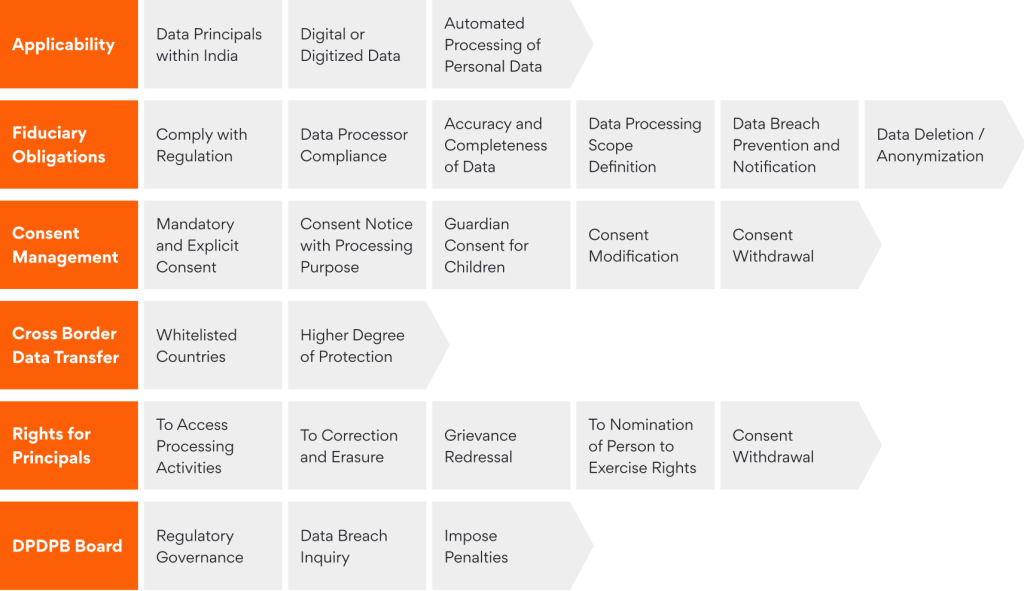
While the compliance burden increases for enterprises, bringing standardization in data protection mechanisms boosts global relevance, and creates:
- Increased customer trust and credibility.
- Improved data management and control over processing activities.
- Transparency and a better understanding of the collected data.
- Improved visibility over business processes and outcomes.
- Organizational accountability and commitment to personal data protection.
- Enhanced enterprise brand value.
How DPDPB Impacts Business as Usual for Insurers
While the tenets outlined in the new data protection law mimic the frameworks set out in IRDAI’s extant guidelines, the burden is much higher for insurers, as the law comes with non-compliance penalties that can go as high as Rs 250 crores or $2.5 billion.
High-level requirements for insurers include:
- Maintaining transparency in personal data processing.
- Securing explicit and free consent from data principles during data collection.
- Clearly defining the purpose of data collection, storage, and processing, and quickly intimating all concerned parties in case of any change.
- Implementing adequate and secure data retention and deletion processes.
- Implementing a process to address data principal data access requests, including withdrawal of consent.
Depending on the insurer and their data, security, and operational practices, these requirements create a new level of mandated compliance that insurers will need to meet in short order – not only for legal reasons, but to ensure and bolster confidence among the customers they serve.
Turning Compliance into a Competitive Advantage
Robust data governance and compliance practices help insurers mitigate privacy risks, avoid data breaches, protect data, and meet compliance objectives. Sustained compliance showcases leadership commitment toward customer centricity and enhances an organization’s security posture, leading to improved market position, brand, and reputation.
Below are some strategies that insurers can utilize to leverage compliance as a competitive advantage, and in tandem ensure compliance with the new data protection law.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactive risk management sustains compliance and helps avoid legal issues, data breaches, penalties, and reputational damages.
- Market Differentiation: Sustained compliance with data privacy regulations showcases a commitment to protecting customer data and enhancing customer trust and loyalty — which in the long-term can translate into a robust market reputation, long-standing customer relationships, and increased business opportunities.
- Continuous Improvement: Routine risk audits help identify and address vulnerabilities before they become incidents, thereby improving an insurer’s overall security posture through enhanced compliance programs.
- Ethical Branding: Demonstrated compliance with ethical business practices emphasizes an organization’s commitment to data transparency, integrity, and accuracy.
- Employee Morale: An organization with a compliance-driven culture and behavior fosters higher employee morale, trust, and productivity, as they recognize that they’re working at a company that places the highest value on protecting customers from risk and themselves from any potential liability or issue.
The Persistent Edge for Compliance
As a digital transformation leader, Persistent has deep expertise in establishing and managing data governance and compliance practices across enterprises with highly complex environments. Our tailor-made data governance suite of solutions, driven by domain experts certified in data governance, help insurers meet the compliance mandates outlined under the new law with:
- Data governance consultation to assess current-state maturity, quality, privacy, and compliance.
- End-to-end data governance, including data cataloging, lineage, classification, business glossary, quality, regulatory compliance assessments, DSAR support, access control governance, data protection, access workflows, and consent management frameworks.
- Ongoing maintenance of business operations, including upkeep of the glossary, creation and maintenance of data catalogs, workflow customization, and governance workflow maintenance.
- Strategic partnerships with leaders in data governance and protection tools and platforms.
Through Persistent’s Data Strategy and Governance offerings, we collaborate with clients to align data with their business goals and assess the maturity of data management functions. We develop a technology roadmap for data-led governance and compliance with privacy regulations. We also work with businesses to carry out data governance programs end to end and tailor them to the needs of the organizations. To learn more about our offerings, get in touch with us here. To learn more about our digital solutions for insurers, click here.








