One of the challenges of drug therapy is that not everyone responds to medications in the same way. This variability in drug response can be influenced by many factors, such as age, weight, diet, lifestyle, and interactions with other drugs. However, another key factor that determines drug response variability is genetics. Genes play an important role in the way we metabolize, transport, and respond to drugs. This field of study is called pharmacogenetics, or pharmacogenomics.
Pharmacogenomics data plays a significant role in precision medicine by associating drug responses to gene variants in a patient. This helps treating physicians to tailor treatment regimens based on a patient’s genetic profile. Assorted studies have shown that the efficacy of the drugs among patients differs based on their gene variants. In this blog, we take a deeper look at pharmacogenomics and the potential impact that Generative AI (GenAI) will have on this emerging field.
Benefits and Current Tools and Resources
Pharmacogenomics can offer many benefits for patients and health care providers, such as:
- Reducing the trial-and-error process of finding the best drug and dose for each patient, which can save time, money, and resources.
- Improving the quality of life and health outcomes of patients by providing more precise and effective treatments.
- Preventing or minimizing the occurrence and severity of adverse drug reactions, which can cause harm, discomfort, or disability to patients.
- Identifying new targets and pathways for drug development, which can lead to the discovery of new and better therapies for various diseases and conditions.
There are plenty of public resources available on pharmacogenomics studies. Some of the well-known databases, tools, and consortia that provide information on pharmacogenomics are:
PharmGKB: The comprehensive Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase which curates and integrates information on genetic variation, drug response, and clinical guidelines. PharmGKB also provides tools for drug dosing, variant annotation, and pathway analysis.
The Pharmacogenomics Research Network (PGRN): The PGRN is a collaborative network of scientists who conduct research on the genomic basis of drug response and adverse effects. PGRN aims to advance the translation of pharmacogenomics into clinical care and improve health outcomes.
The Pharmacogenomics Mutation Database (PGMD): The PGMD is a comprehensive database that collects and annotates human genetic variants associated with drug response and toxicity. PGMD also provides tools for variant filtering, prioritization, and visualization.
The Pharmacogene Variation Consortium (PharmVar): PharmVar is an international consortium that defines and maintains a high-quality and standardized catalog of pharmacogene alleles and haplotypes. PharmVar also provides tools for pharmacogene genotyping, nomenclature, and interpretation.
The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC): The CPIC is an international group of clinicians, researchers, and pharmacists who develop evidence-based guidelines for the implementation of pharmacogenomic testing in clinical practice. CPIC guidelines provide recommendations on how to adjust drug therapy based on genotype results.
Although all these resources are respected and widely used, Persistent is focused on creating a positive impact on patient care and personalized medicine by providing easy access to the comprehensive CPIC guidelines with GenAI.
Virtual Assistant for Better Patient Outcomes
A significant development in pharmacogenomics is the creation and application of pharmacogenomic guidelines that can offer evidence-based and standardized advice for the use of pharmacogenomics testing and interpretation in clinical practice. In this context, CPIC is a useful tool for personalized medicine, as it connects pharmacogenetic research with the clinical practice, is regularly updated to reflect new evidence and feedback, and its guidelines are based on rigorous review of available scientific literature and expert consensus. CPIC guidelines can assist healthcare providers and patients to make informed choices about drug therapy based on genetic information and thus can also enhance the safety and effectiveness of drug treatment, lower adverse drug reactions, and improve the quality of patient care.
Currently, the CPIC database provides guidelines for 151 drugs targeting 29 unique genes across multiple disorders. Although the guidelines follow a standard format, they are text-intensive and require substantial manual efforts to fetch required information efficiently. Integration of GenAI technology into clinical practices can enable access to complex pharmacogenetics data that normally might take days to locate and interpret, and overall enhance patient care. To speed up clinical testing and result interpretation, we focused on making these guidelines easily accessible by deploying a GenAI-powered solution. We utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) and context-aware GPT models to develop BioMedInsights-PGx, a virtual assistant that can derive faster biomedical insights from large textual information. A Retrieval Augmented Generative (RAG) approach was used with GPT3.5-Turbo model to provide context-specific answers to users’ queries on pharmacogenetics test results (See Figure 1).

Here is a sample conversation between BioMedInsights-PGx and a medical professional looking for specific information based on CPIC pharmacogenomics clinical guidelines:
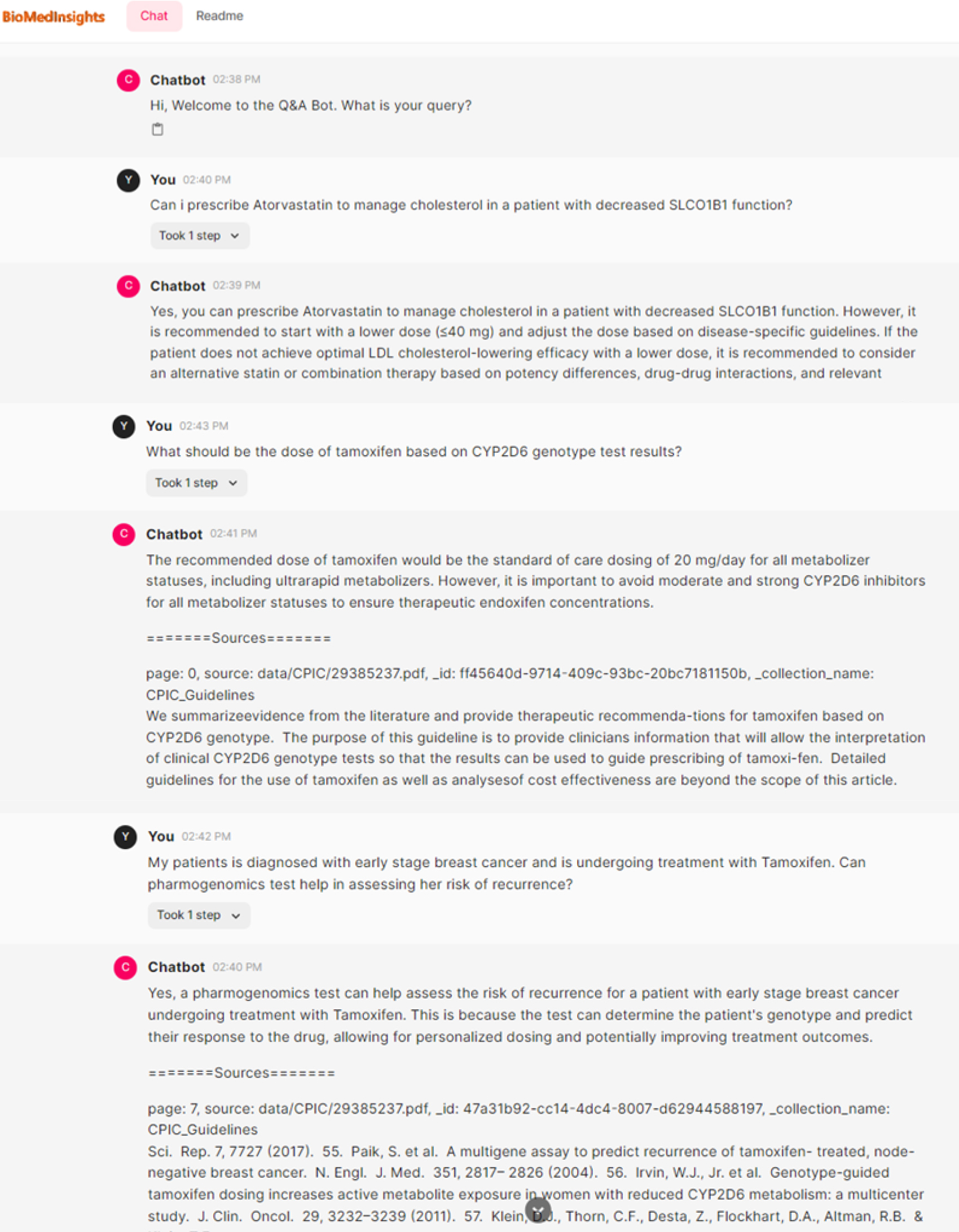
In our application, we have fine-tuned the parameters of the GPT model to ensure that answers are accurate and are derived only from the validated documents provided, with minimal or no hallucinations. The generated answers are supported by relevant references to further validate the sources of the generated summaries to ensure safe clinical practice.
The BioMedInsights-PGx app is user-friendly and can be customized for different personas to help select the correct drug and dosage. It represents GenAI’s potential to transform clinical practice and genetic counseling. Although we caution that answers provided by the assistant do not constitute medical advice, BioMedInsights – PGx can create a significant impact in expediting pharmacogenomics-based treatment regimen and improve patient care. What’s more, the same principles for creating the CPIC personal assistant can be extended to support other associated pharmacogenomics domains and datasets, which can be easily scaled and offer a consolidated platform to empower clinicians and physicians for quick insights. To know more about our solutions that leverage Generative AI for Healthcare and Lifesciences, such as our virtual assistant, reach out to us.
Authors’ Profile
Indhupriya Subramanian
Project Lead – Domain, Corporate CTO Organization
Anamika Krishanpal
PhD, Principal Domain Expert, Life Sciences R&D, Corporate CTO Organization
Related Content
Contact us
(*) Asterisk denotes mandatory fields








