Service as Software is a model where agents and agentic workflows make autonomous decisions, drive dynamism, and render services just as humans would. The cognitive load, which had hitherto remained exclusive to human intelligence, is now mastered by AI, making it possible for agents (or software) to deliver services that humans traditionally did.
But if AI has existed for more than half a century, what took agents this long to mimic human decision-making?
As it evolved, AI got better at highly specific tasks, which is why it was called narrow AI. As GenAI broke into the scene, general-purpose AI could answer questions and generate human-like original content. Mapping the last three years of the AI trajectory, AI improved at handling jobs with tools and patterns like reflection, ushering in the next wave of AI that can autonomously take up general tasks as agents.
Agentic AI involves multiple task-specific jobs, working in cohesion and collaborating with other agents to solve complex end-to-end business problems.
Counterbalancing Pairs for AI-Human Collaboration
Enterprises are always looking to make systems and processes more efficient. Agentic AI enables businesses to rethink workflows without the constraint of human cognitive load, empowering them to build new processes to drive outcomes faster, better, and cheaper.
Simply put, counterbalancing is equal but opposite effects such that it does not affect the parent characteristic. Suppose the characteristic is a service that was traditionally rendered by humans and AI (as software). By introducing some human-like features in AI and removing the same from humans, such as the cognitive load, we can counterbalance AI-human collaboration to enhance service delivery further. These are a few examples of counterbalancing pairs:
- Control: Traditionally, narrow AI and humans have been the two essential pillars of service delivery. The AI system must have a definite goal orientation to convert narrow AI to agentic AI. However, with this goal orientation, a human will no longer need to exercise stringent control. Therefore, goal orientation from an AI perspective counterbalances stringent control from a human perspective, essentially removing control and transferring it to an AI system by orienting the goal toward the desired end outcome.
- Task Planning: Human intervention is limited in scope when an agent takes care of task planning and process orchestration. The ability of agents to act dynamically based on changing requirements and design workflows on the fly is an essential trait humans have in a non-autonomous world.
- Error Identification: Through evolution and reflection based on historical evidence, agentic AI can identify an error and change the work structure based on feedback, essentially counterbalancing the component of error correction that humans used to do.
- Contextual Understanding: The agents’ understanding of contextual knowledge leads to lesser cognitive investment from a human since now agents can comprehend the context, decide, and act based on it.
- Guardrails: As humans oversee AI, agents must also have defined guardrails to limit actions in specific work areas and comply with regulations and standards predefined or intelligently identified to make ethical decisions. System Architects must ensure that the human-in-loop checkpoints are in place and humans are presented within the context for an informed decision.
Service as Software: Re(AI)magining Human-AI Collaboration
Transforming the future of work via cognitive Architecture
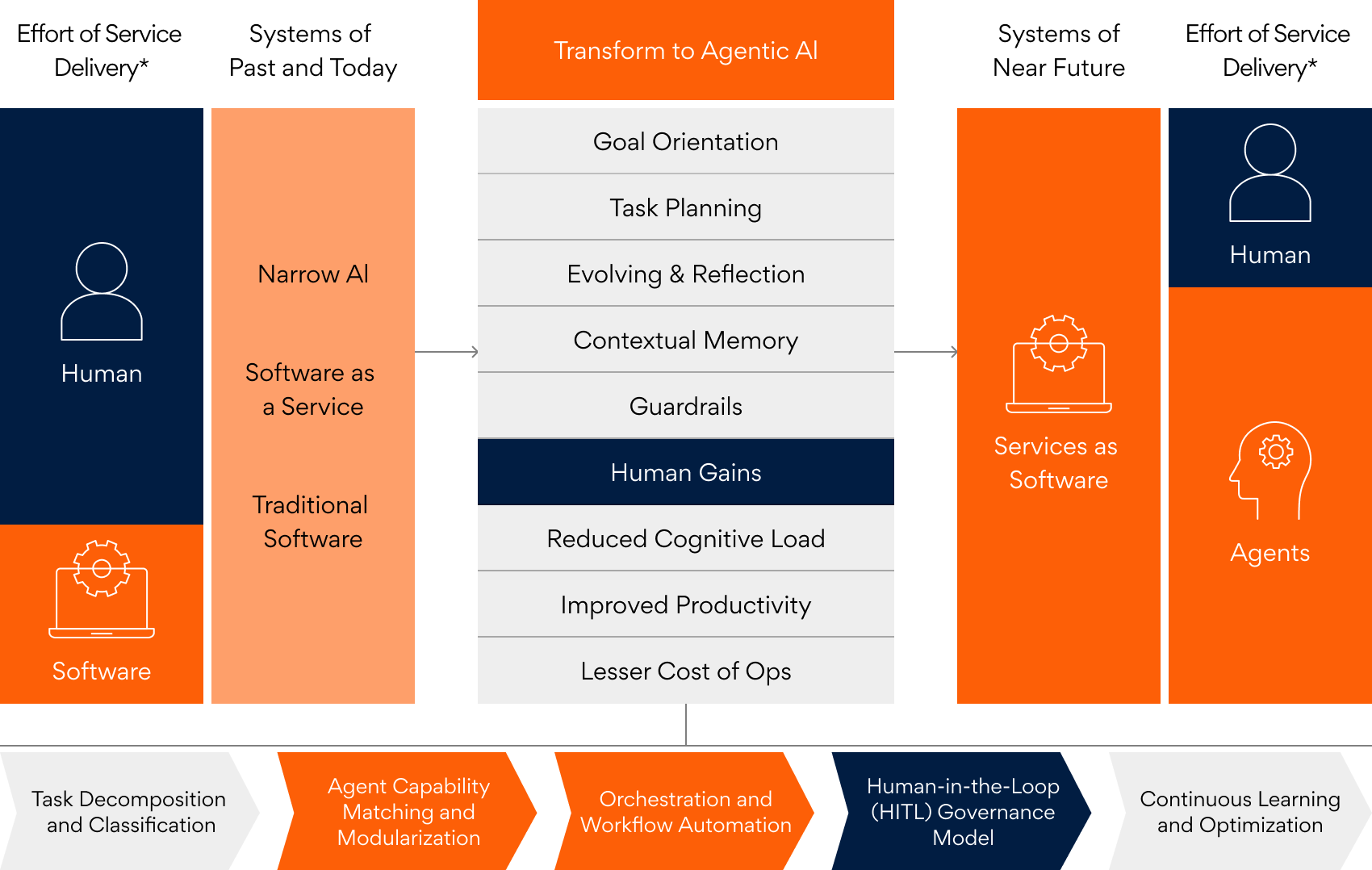
Transferring these cognitive tasks previously reserved for humans to agents marks the genesis of service as software, where agentic AI performs nearly all functions that a human once did.
Re(AI)magining Business Processes with Agentic AI
Consider a Property and Casualty (P&C) insurance underwriting workflow powered by Agentic AI. Tasks like document cognition, risk intelligence, survey, and recommendation engine would be taken care by agents. An orchestrator agent would plan an agentic workflow for individual proposals based on input coginition. Human underwriters would be at the end of the workflow to review and green-light agent recommendations. With potentially more than 60-70% of the straight-through processing handled by agents, the human underwriter has outsourced the cognitive load to the AI, creating more room for value-adding actions. This increases the volume of proposals processed, and the human underwriter comes in to help with complex proposals where agents cannot make a decision.
At Persistent, we are transforming the future of work and services through a cognitive architecture powered by agentic workflows and agents that autonomously make decisions and automate job functions end to end – transitioning from narrow AI to agentic AI.
The power to offload human cognitive load has thinned the lines between services and software. Connect with us to reimagine your workflows and transform your business with agentic workflows.
Author’s Profile
Dattaraj Rao
Chief Data Scientist, AI Research Lab
Arun Kishorre Sannasi
Senior Consulting Expert, Persistent Systems








