(Image Credit Apple)
In our previous article, we talked about how spatial computing plays a significant role in building the Extended Reality (XR) experiences. In this article, we will talk about Apple Vision Pro – Apple’s Spatial computer and the transformative power of Apple’s visionOS in shaping the future of spatial design.
Apple Vision Pro

Launched on June 5th, 2023, Apple Vision Pro enables the blending of digital data and physical world surrounding the users, providing an interactive and immersive experience and allows users to experience Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR) and Virtual Reality (VR) applications.
It has high-resolution displays with powerful Apple silicon chips – M2 which deliver amazing performance and R1 that processes information from 12 cameras, 6 microphones and 5 sensors. These help eliminate delays between display and sensor, resulting in superior performance. More natural and intuitive inputs via eye tracking, voice commands and hand gestures allow users to control and interact with the three-dimensional (3D) user interface.
Designing for Apple’s visionOS
Apple Vision Pro is a Mixed Reality headset that enables smooth and seamless blending of both digital and physical worlds. Users get unlimited 3D space to engage, interact and experience applications and can stay connected to their surroundings while experiencing these applications.
visionOS – the world’s first spatial operating system that powers Apple Vision Pro, enables users to interact with the digital data while being in their physical space, making the experiences more intuitive and immersive.
Building blocks that make up spatial computing in Apple’s visionOS –
- Windows – One can create multiple windows in space in the visionOS app, which can be built using SwiftUI. This is for displaying 2D content and web pages with familiar elements such as views, controls, etc.
- Volumes – These can display 3D content using Apple’s Realitykit, which is a 3D framework that can seamlessly blend virtual objects in real world in the scenes.
- Spaces – Apps can launch into a Shared Space – where different apps can be set beside each other. Apps can also be launched in dedicated Full Space – where an app can be experienced by the user in the entire space. These spaces offer a focused view for the user and also support complete immersion. It all depends on the use cases and experiences one wants to build. Dedicated Full space experiences will likely take more precedence as they will help users focus on their tasks.
Immersion
Immersive experiences blend physical and digital worlds and enable users to experience the digital world with all of their senses while being in the physical world. Spatial experiences consist of different levels of immersion and an app in Vision Pro can smoothly transition from one level to other.
There are three types of immersion –
- Full – It provides fully immersive experiences to the users.
- Mixed – It helps blending real world with the virtual content.
- Progressive – Users can use Digital Crown to resize the portal in which they are immersed in, from their initial 180-degree view of the content. Thus, with this control of immersive experience, users get more enhanced experiences.
To further enhance immersion, one can include spatial sound, which creates a more realistic and intuitive experience with audio that changes with the user’s orientation and position in the real environment.
Apple Vision Pro enables users to adjust the immersion level to create more comfortable and engaging experiences, as not all experiences need to be fully immersive.
Layout and Design
To display the 2D or 3D content in the 3D space, the default and most important content must be presented in front of the user’s field of view, that is the comfortable viewing space without head movement. The less important content should be displayed at the edges or below the field of view to avoid interfering with the primary experience, while still being accessible.
When building applications, keeping the interactive content at the same depth ensures a seamless user experience even after switching UIs. The right size for the controls is decided based on the concept of points – a measurement based on screen resolutions. It is recommended to allocate a minimum of 60 points of space for each element to ensure that the UI adheres to design guidelines for eye targets and enhances the user experience by making the UI more comfortable to view.
Interaction
Users can interact with their eyes, hands, and voice by looking at the different elements and tapping their fingers. There is also a ‘Dwell control’ feature where the users can select an element with their eyes. Additionally, there is an option to reach out and select the element directly by touching it.
Apple emphasizes indirect gestures like ‘gazing’ followed by a ‘tap gesture’ to interact with virtual objects instead of direct interactions, which are better suited where quick interactions are not critical.
Audio is essential for creating an immersive experience and helps users interact more effectively.
Audio sources can be:
- Spatial audio – Has position and direction. It is experienced based on the position and direction of the object it is associated with.
- Ambient audio – Has only direction. Experience based on direction, e.g., the wind coming from east or west where only the direction matters.
- Channel audio – Has no positional or directional attributes, making it ideal for experiences requiring background music
Spatial sound helps create an immersive spatial experience design that’s lively and compelling.
Building XR experiences for Apple Vision Pro
With its powerful features and capabilities, Apple Vision Pro offers a wide range of possibilities for creating engaging XR experiences. As mentioned above, with the ‘Digital Crown’, users can control the level of immersion that enables a range of XR experiences from AR, MR to fully immersive VR. Accordingly, based on use cases, interactions required, related digital content, immersion levels, and spaces, one can build XR experiences for Apple Vision Pro.
Following high-level steps can be followed based on the use-cases
- Import assets and models – Load the necessary assets and 3D models into the scene. Use high-quality textures and materials to enhance the realism of the virtual objects. Apply glass morphism as required to smoothly blend in with the surroundings of the experience.
- Configure lighting and shading – Adjust the lighting settings to match the desired atmosphere and mood. Experiment with different light sources and shadow effects to create depth and volume. With visionOS, apps can react to lighting and cast shadows.
- Add interactions and animations – Add in the behaviors and actions of your virtual objects as required in the use case. Implement indirect / direct gestures, voice commands, spatial audio or other input methods to enable users to interact with your XR experience.
- Immersion – Apply immersion levels as required – not necessarily full immersion needs to be added for every experience. The more the users can feel and see their physical surroundings, the more comfortable the experience tends to be.
- Test and refine – Iterate over your work, testing and refining until you achieve the desired results. Debug issues, adjust parameters, and fine-tune the performance of your application.
- Optimize for performance – Ensure that your XR experience is built using accelerators to streamline content creation, at Persistent we have built XRGen accelerator powered by GenAI. It ensures that your XR experience runs with optimized graphics rendering and 3D models, reduce memory usage, and minimized lag.
At Persistent, we help businesses build different customized XR experiences using multiple digital formats with assets, 3D models and simulations added to provide more immersive and interactive experiences.
Refer Fig. 2 below that gives a glimpse of one such Mixed Reality experience designed and built for Apple Vision Pro. User is able to experience this around the physical space, he is present in. Using indirect gesture like ‘gazing’ at the ‘View’ button followed by a ‘tap gesture’, the user can interact with the digital content and view different simulations built for the use case.
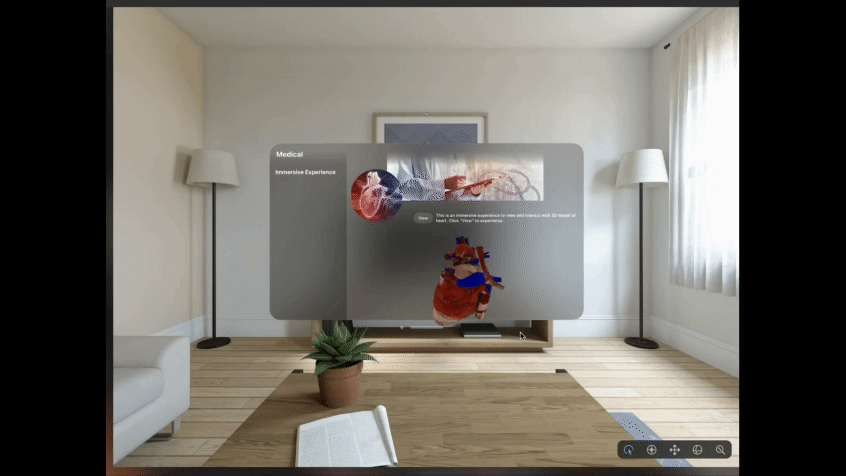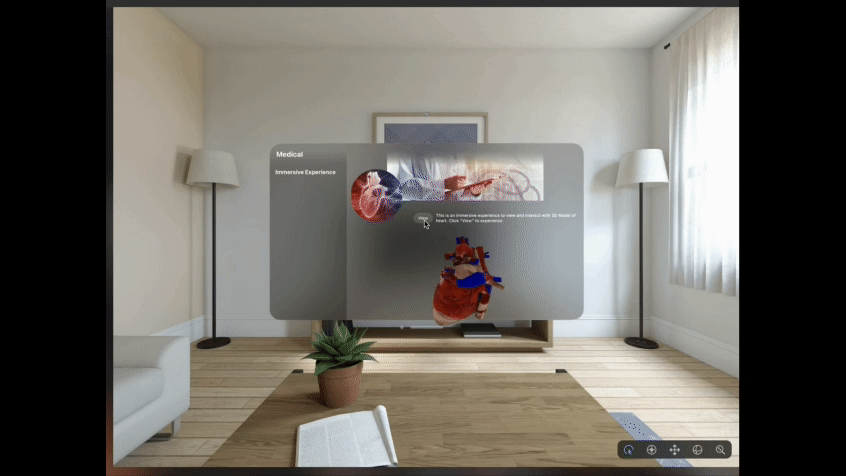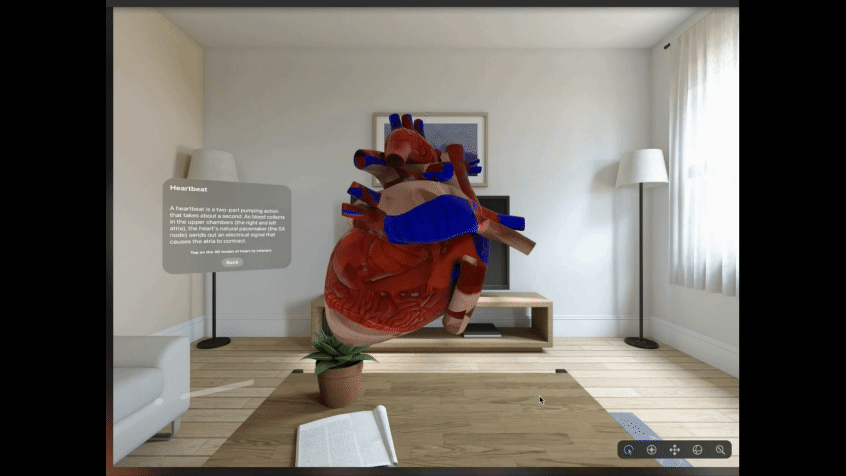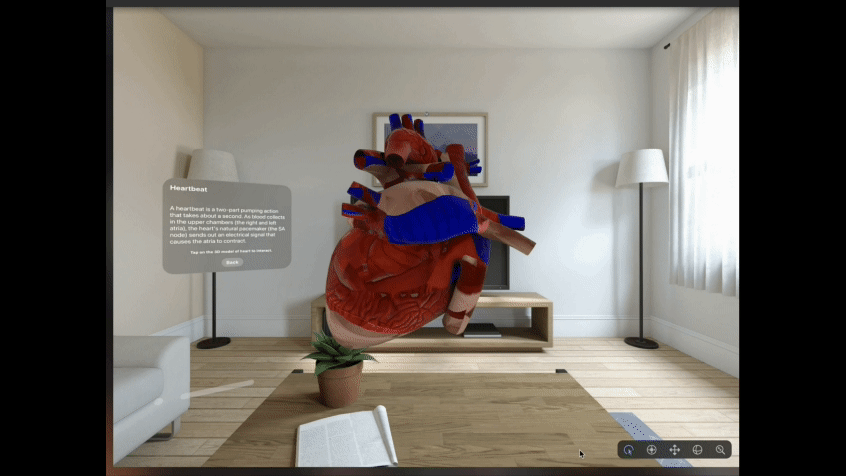
We leverage all the available XR platforms, tools and packages to create XR experiences for different use cases across industry sectors like Healthcare, Manufacturing, Retail, Telecommunication, etc.
Our XR solutions cater to different challenges faced in these industries for various use cases:
- Operations and troubleshooting processes
- Complex production processes
- Field support
- Different product experiences along with guidance
By harnessing these XR technologies, Persistent helps businesses deliver outstanding experiences which –
- Improve efficiency
- Improve productivity
- Reduce costs
- Provide enhanced intuitive user interactions
With deep expertise in XR technologies and building different AR, VR and MR solutions, Persistent helps organizations build customized, intuitive and immersive experiences. We provide XR development, consultancy and design services and support to our clients.
For more information on Google Platform for Extended Reality, please reach out to us.
References – https://www.apple.com/in/newsroom/2023/06/introducing-apple-vision-pro/
Author’s Profile
Shilpa Ramteke
Head, Extended Reality







